Amb. Huckabee Claims Israel Has 'Biblical Right' To Conquer Whole Middle East
In a jaw-dropping exchange with Tucker Carlson, US Ambassador to Israel Mike Huckabee openly framed Israel's territorial claims in biblical terms - suggesting the Jewish state has a divine mandate over virtually the entire region.
Asked whether a passage from the Book of Genesis could be read as granting Israel the right to claim all the land between Egypt's Nile River and Syria's Euphrates, Huckabee didn't hedge. He bluntly and without apology said it would be "fine" if Israel and its military took over the whole Middle East. Full interview can be accessed here:
The Mike Huckabee interview, and the truth about America’s deeply unhealthy relationship with Israel.
— Tucker Carlson (@TuckerCarlson) February 21, 2026
(0:00) Why We Were Interrogated in Israel
(25:38) Why Did Huckabee Meet With American Traitor Jonathan Pollard?
(34:26) Has Huckabee Advocated to Extradite Sex Offenders Who… pic.twitter.com/SDIf9TzdiR
"It would be fine if they took it all," Huckabee, a former Southern Baptist Minister and previously the governor of Arkansas made clear. This led to a wide ranging conversation and back and forth over whether the modern nation-state of Israel, officially founded as a sovereign government on May 14, 1948, is synonymous with the Israel written about in the Old Testament, stretching back thousands of years.
Here's how that contentious segment of the interview unfolded, according to a transcript and commentary:
Huckabee was asked in an interview with US conservative commentator Tucker Carlson about his understanding of a biblical verse suggesting that land including parts of Egypt, Syria and Iraq had been divinely promised to the Jewish people.
Carlson said that according to the Old Testament, the boundaries would be “basically the entire Middle East.”
He continued: “Does Israel have the right to that land?”
“Not sure we’d go that far,” Huckabee said in reply. “It would be a big piece of land.”
Carlson then pressed him: “Does Israel have the right to that land?”
“It would be fine if they took it all,” Huckabee responded, before adding, “I don’t think that’s what we’re talking about here today.”
Carlson asked: “You think it would be fine if the state of Israel took over all of Jordan?”
That's when Amb. Huckabee must have realized he was entering some hot diplomatic water, which would be sure to outrage Washington's Arab allies in the region.
"They’re not trying to take over Jordan. They're not trying to take over Syria. They’re not trying to take over Iraq or anywhere else, but they do want to protect their people," Huckabee responded. We should note here that the Israeli army has indeed invaded southern Syria and is occupying swathes of territory which lie a mere dozen or so miles from Damascus.
TUCKER: “How much does it matter what Americans think?”
— African (@ali_naka) February 21, 2026
AMB. HUCKABEE: “It matters every bit.”
TUCKER: “80% oppose war with Iran.”
AMB. HUCKABEE: “We don’t live in a world where polls dictate policy.”
TUCKER: “Oh, I thought you said it matters what Americans think.”
This is… pic.twitter.com/LFiEk32Mna
"I think you’re missing something because they’re not asking to go back to take all of that, but they are asking to at least take the land that they now occupy, they now live in, they now own legitimately, and it is a safe haven for them," Huckabee added.
Huckabee on Saturday, the day after the Carlson interview aired, issued a lengthy clarification of his comments, accusing the former Fox show host of twisting his words and engaging in bad faith arguments and attacks.
Tucker and I had a very twisty and frankly confusing discussion about the meaning of Zionism.
— Ambassador Mike Huckabee (@GovMikeHuckabee) February 21, 2026
Now, I have no idea if Tucker was trying to be difficult or we were just talking past each other, but he started out the discussion on Zionism by saying he wanted to ask me in my…
There are many parts of the rare interview which will be sure to spark lasting debate. Supporters of Huckabee tend to cast any and all criticisms of Israeli policy as 'anti-Semitic' - while critics of Tel Aviv point out that being against political Zionism does not equate to being anti-Jewish in any way.
Tyler Durden Sat, 02/21/2026 - 22:45

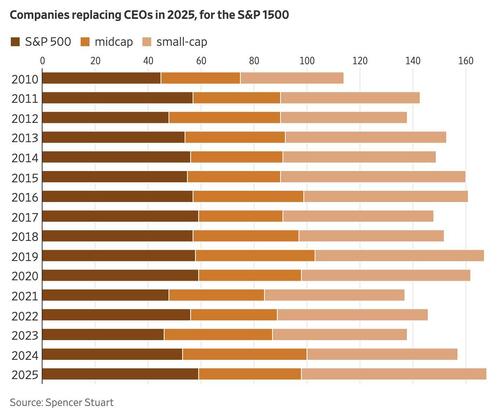
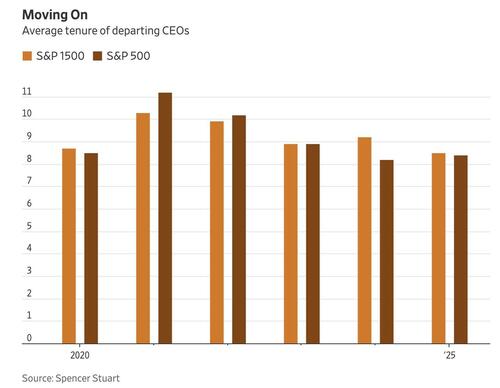
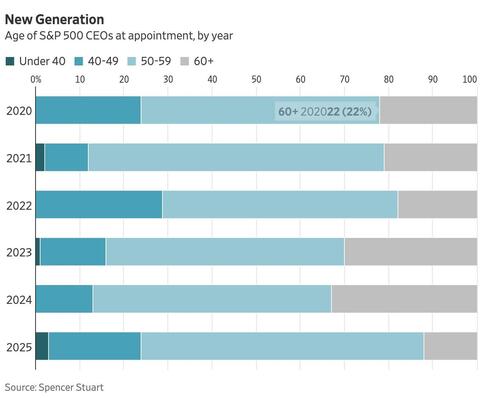
 A truck drives through the Port of Oakland in Oakland, Calif., on Nov. 14, 2025. Justin Sullivan/Getty Images
A truck drives through the Port of Oakland in Oakland, Calif., on Nov. 14, 2025. Justin Sullivan/Getty Images




 via Iranian state media
via Iranian state media



 Source: qantara.de
Source: qantara.de


 The IRS in Washington. Madalina Kilroy/The Epoch Times
The IRS in Washington. Madalina Kilroy/The Epoch Times
Recent comments